exercise 11 :: Electronic structure of graphene and its Wannierization
The exercise demonstrates calculation of electronic band structure of graphene and maximally localized Wannier functions (MLWF) using wannier90 package.
TASK 01
Consider graphene with nearest neighbor carbon atom distance of 1.42 Angstrom and sheet separation of 12 Angstrom in order to model a single sheet. The input for scf calculations could look like:
&control
title = 'graphene, c=12 AA vacuum' ,
calculation = 'scf' ,
restart_mode = 'from_scratch' ,
outdir = './tmp/' ,
pseudo_dir = './' ,
prefix = 'graphene' ,
verbosity = 'high' ,
/
&system
ibrav = 4,
celldm(1) = 4.647806, celldm(3) = 4.87901473571,
occupations = 'smearing', smearing = 'm-v', degauss = 0.0001,
nat = 2,
ntyp = 1,
ecutwfc = 40, ecutrho = 160 ,
nbnd = 16,
/
&electrons
conv_thr = 1.0d-8,
/
ATOMIC_SPECIES
C 12.01078 C.pbe-mt_fhi.UPF
ATOMIC_POSITIONS crystal
C 0.333333333 0.666666667 0.000000000
C 0.666666667 0.333333333 0.000000000
K_POINTS automatic
12 12 1 0 0 0
Perform scf calculations to obtain ground state electronic density and then perform bands calculations along high symmetry lines connecting K--M-K points in first Brillouin zone. For coordinates of the high symmetry points see this website. The resulting band structure is show in the following figure.
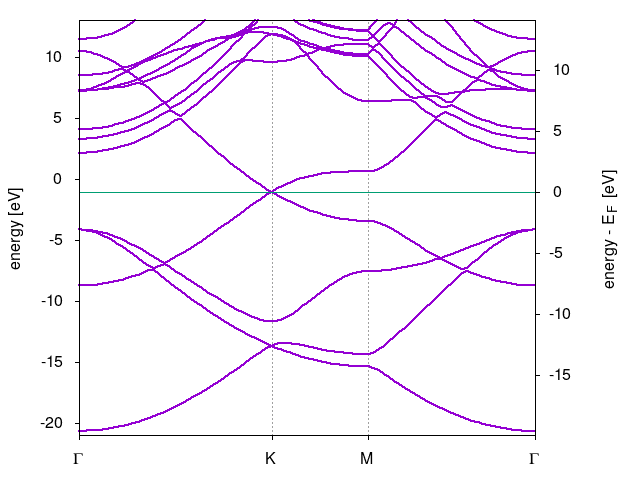
TASK 02
Investigate electronic states forming the occupied band that crosses at the K point in the so called Dirac point. For this purpose calculate electronic density in real space for the state at the point for energy of about -7.5 eV below the Fermi energy, and for the K point state at the Fermi energy. For this purpose perform nscf calculations for the and K points only specifying:
K_POINTS crystal
2
0.00000000 0.00000000 0.0 1
0.33333333 0.33333333 0.0 1
The output file should contain the following information
k = 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 ( 1833 PWs) bands (ev):
-20.6556 -8.7365 -4.1598 -4.1598 2.1188 3.2694 4.0444 7.2084
7.2614 7.2614 8.4672 10.4427 11.4584 13.4540 15.2730 21.4718
occupation numbers
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
k = 0.3333 0.5774 0.0000 ( 1779 PWs) bands (ev):
-13.6864 -13.6864 -11.6861 -1.0728 -1.0728 9.5744 11.8605 11.8605
12.4498 14.0514 14.0514 14.1746 14.1746 14.5703 15.2441 15.7374
occupation numbers
1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 0.5000 0.5000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
the Fermi energy is -1.0726 ev
Where you can see that we are interested for the second state at the point fourth state at the K point. Now we are about to perform the electronic density plot in real space using pp.x program. The input for the electronic density of the state at at energy about -7.5 eV could look like:
&inputpp
prefix = 'graphene'
outdir='./tmp/',
filplot = 'tmp.G2',
plot_num = 7,
spin_component = 0,
kpoint(1) = 1,
kband(1) = 2,
kband(2) = 2,
/
&plot
nfile=1
filepp(1)='tmp.G2', weight(1)=1.0
iflag=3
output_format=3
e1(1)=1.0, e1(2)=0.0, e1(3)=0.0
e2(1)=0.0, e2(2)=1.73205, e2(3)=0.0
e3(1)=0.0, e3(2)=0.0, e3(3)=1.0
x0(1)=0.0, x0(2)=0.0, x0(3)=-0.5
nx=60, ny=110, nz=60
fileout='edp_G-point_E-7.5eV.xsf'
/
For further input description see the link. Similarly you can calculate electronic density in real space for the state at the fourth band at the K point. Obtained xsf files can be visualized, e.g., with VESTA providing the following plots. One can see that both the states are similar to atomic orbital suggesting that the band is formed by the conjugate -electrons of carbon.
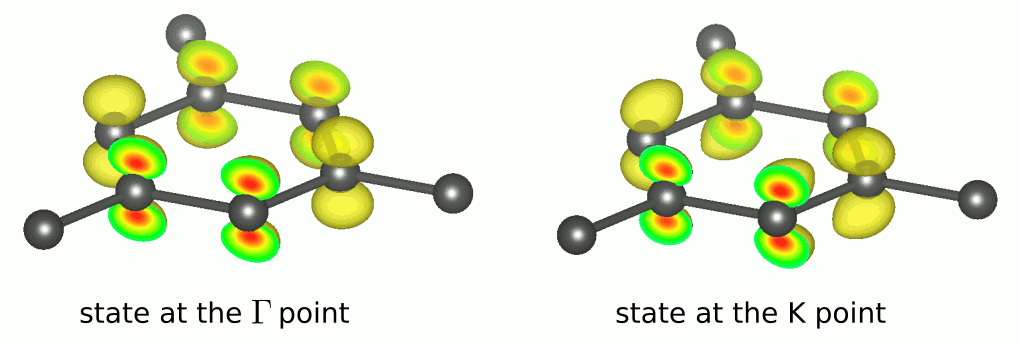
TASK 03
Wannierize the -bands of graphene using Wannier90 package.
-
perform
nscfcalculation with setting the following flag:wf_collect = .true.;nosym = .true.in the input file for k-points generated on grid usingkmeshutility:
$PATH_TO_WANNIER90_CODE/utility/kmesh.pl 12 12 1and use the k-point list placing it to theK_POINTSblock of yournscfinput file. -
pre-process for Wannierization. Use provided example input file for wannier90. For further details of the input flags refer to user guide.
!---------------------------GENERAL num_bands = 16 num_wann = 2 !------------------------------CONV iprint = 3 num_iter = 500 num_print_cycles = 50 !!! -- Disentanglement parameters -- !!! dis_froz_min = -3.0 dis_froz_max = 2.0 dis_win_min = -10.0 dis_win_max = 11.0 !-----------------------------bands !restart = plot bands_plot = .true. !wannier_plot = .false. write_hr = .true. begin kpoint_path G 0.0 0.0 0.0 K 0.333333 0.333333 0.0 K 0.333333 0.333333 0.0 M 0.5 0.0 0.0 M 0.5 0.0 0.0 G 0.0 0.0 0.0 end kpoint_path !----------------------------SYSTEM begin unit_cell_cart bohr 4.647806 0.000000 0.000000 -2.323903 4.025118 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 22.676715 end unit_cell_cart begin atoms_frac C 0.333333333 0.666666666 0.000000000 C 0.666666666 0.333333333 0.000000000 end atoms_frac begin projections C:pz end projections spinors = false !----------------------------KPOINTS mp_grid : 12 12 1 begin kpoints 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.08333333 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.16666667 0.00000000 . . . {k point coordinates are those generated by the kmesh.pl} end kpointsThe
num_bands,num_wann,unit_cell_cartandatoms_fraccan be taken from thescfornscfoutput files. Forprojectionswe consider the orbitals andmp_gridshould be the same list as used fornscfcalculations generated by thekmesh.pl 12 12 1 wanscript. Save the above input ascase.win.
Run the pre-processing:wannier90.x -pp caseto generatecase.nnkpfile needed for further step. -
Run
pw2wannier.x < pw2wann.in > out.pw2wanto compute overlaps between the Bloch states and the projections of the starting guess (written in thecase.mmnandcase.amnfiles). The input filepw2wann.inshould look like:&inputpp outdir = './tmp' prefix = 'graphene' seedname = 'case' write_mmn = .true. write_amn = .true. write_spn = .true. write_unk = .false. / -
Perform Wannierization by computing the MLWFs:
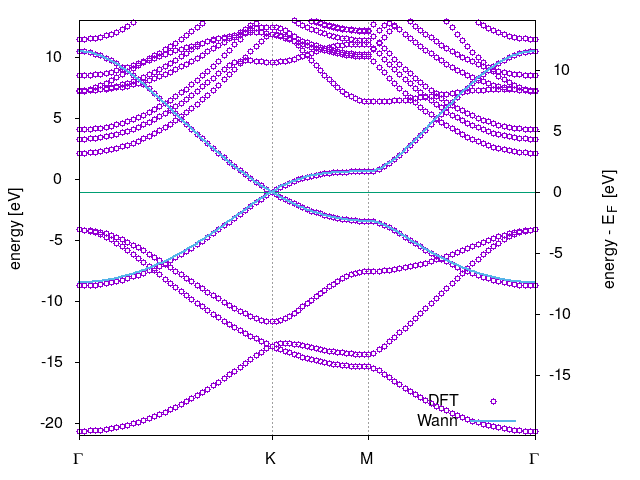
wannier90.x case. Check your Wannierization by plotting thecase_band.datover the DFT band structure. In the figure below the Wannierized energy dispersions of the -bands are shown with (blue) lines over the DFT data (open circles).
Martin Gmitra :: martin.gmitra@upjs.sk
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.